Welcome
back to 'India Study Solution’ Physics MCQ Test Series /
Practice Questions Section, This section contains MCQ and Objective Test Series each set containing
10 most important questions with hints & solutions from the chapter KINEMATICS (syllabus included below).
Question 24: The displacement of a body is given by s = (gt2)/2, where ‘g’ is acceleration due to gravity. The velocity of the body at any instant ‘t’ is given by -
Physics
Notes and Study Materials with Key Points to remember and important Formulae
and more on Kinematics - Motion in a straight line, Uniform and Non-uniform
acceleration, Relative velocity, Scalars and Vectors and all topics in syllabus
(provided at the end of hints / solutions) will be published separately (link for which will be provided here)
Kinematics:
Physics Guide and Solution
MCQ Test Series – Set 3
(Q. No.21-30)
Question
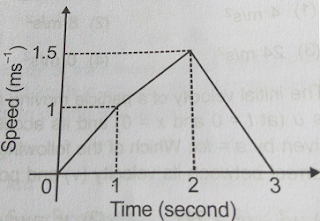
21: The speed-time graph of an object moving along a solid curve is shown in
the adjacent fig. The distance traversed by the object from t - 0 to t = 3 is -
a. 10/2 m
a. 10/2 m
b.
10/4 m
c.
10/3 m
d.
10/5 m
Question
22: The slope of velocity-time graph for uniform motion of an object is -
a.
unity
b.
zero
c.
infinite
d.
more than unity with some finite value
Question
23: A point mass starts moving in a straight line with constant acceleration f
from rest
at t =0. At time t = 2s, the acceleration changes
the sign, remaining the same in magnitude. The mass returns to the initial
position at time t = t0 after start of motion.
Here t0 is:
a.
4s
b.
(4 + 2√2)s
c.
(2 + 2√2)s
d.
(4 + 4√2)s
Post continues after the Ad -
Question 24: The displacement of a body is given by s = (gt2)/2, where ‘g’ is acceleration due to gravity. The velocity of the body at any instant ‘t’ is given by -
a.
(gt3)/6
b.
(gt2)/2
c.
gt
d.
(gt)/2
Question
25: Two particles start from rest simultaneously and are equally accelerated.
Throughout the motion, the relative velocity of one with respect to other is
-
a.
zero
b.
non-zero and directed parallel to acceleration
c.
non-zero and directed opposite to acceleration
d.
directed perpendicular to the acceleration
Question
26: A particle moves with uniform acceleration and v1, v2
and v3 denote the average velocities in the three successive
intervals of time t1, t2 and t3. Which of the
following relations is correct?
a.
(v1 – v2) : (v2 – v3) = (t1
– t2) : (t2 + t3)
b.
(v1 – v2) : (v2 – v3) = (t1
+ t2) : (t2 + t3)
c.
(v1 – v2) : (v2 – v3) = (t1
– t2) : (t1 – t3)
d.
(v1 – v2) : (v2 – v3) = (t1
– t2) : (t2 – t3)
Question
27: The vertical height of point P above the ground is twice of that of Q. A stone
is projected downward with a speed of 5 m/s from P and at the same time another
stone is projected upward with the same speed from Q. Both stone reach the
ground simultaneously, then -
a.
PQ = 30 m
b.
Time of flight of stones = 3 s
c.
Both (a) and (b) are correct
d.
Both (a) and (b) are wrong
Question
28: Which of the following position-time graphs shows an object moving with
negative acceleration?
Question 29: The total vertical distance covered by a freely falling body in a given time is directly proportional to -
Question 29: The total vertical distance covered by a freely falling body in a given time is directly proportional to -
a.
time
b.
square of time
c.
square of acceleration due to gravity
d.
product of the time and acceleration due to gravity
Question
30: A 100 m long train crosses a man travelling at 5 km/h, in opposite
direction, in 7.2 s, then the velocity of the train is -
a.
40 km/s
b.
25 km/s
c.
20 km/s
d.
45 km/s
Physics Guide and
Solution: KINEMATICS
Hints
& Solutions of Practice Questions / MCQ Test Series – Set 3 (Q. No.21–30)
Answer 21: b. Answer 22: b.
Answer 25: a. (Hint: They will have
the same velocity at all instants and hence, their relative velocity is zero.)
Frame of
reference, Motion in a straight line, Uniform and Non-uniform motion, Average
speed and instantaneous velocity, Uniformly accelerated motion, Velocity -
Time, Position - Time graphs, Relations for uniformly accelerated motion,
Relative velocity, Motion in a plane.
Scalars
and Vectors, Vector addition and subtraction, Zero vector, Scalar and vector
products, Unit vector, Resolution of a vector, Position and Displacement
vector, General vector and notation, Equality of vector, Multiplication of
vector and a real number.
Please
click on the link below for more solved Test Series on Kinematics, confidence
boosting practice questions with hints and answers for preparing NEET, AIPMT,
JEE Main, Medical, Dental Entrance Exams, Engineering Entrance Exams; MBBS and
Engineering Admission Tests, NTSE, KVPY and other competitive exams.
If
you like this post then, please leave a feedback in the comment box to
encourage us.
KINEMATICS - India Study Solution Test Series Questions